There are many agile development methods; most minimize risk by developing software in short amount of time. Software developed during one unit of time is referred to as an iteration, which may last from one to four weeks. Each iteration is an entire software project, including planning, requirements analysis, design, coding, testing, and documentation. An iteration may not add enough functionality to warrant releasing the product to market but the goal is to have an available release (without bugs) at the end of each iteration. At the end of each iteration, the team re-evaluates project priorities.
Agile methods emphasize face-to-face communication over written documents. Most agile teams are located in a single open office sometimes referred to as a bullpen. At a minimum, this includes programmers and their customers. The office may have testers, interaction designers, technical writers and managers.
Agile methods also emphasize working software as the primary measure of progress. Combined with the preference for face-to-face communication, agile methods produce very written documentation relative to other methods.
Advantages of using Agile
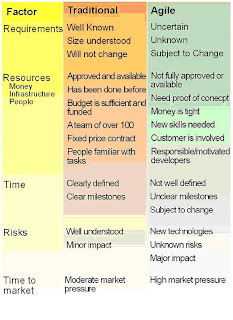
Agile approaches are good when your requirements are uncertain. In this case, agile processes may be uncomfortable, but will be more effective. By embracing the change and planning for it, agile processes lower this risk.
most project plans that imply a guaranteed delivery date, cost, and functionality are either wrong, heavily padded, or both. Agile processes open up the current status of the project to a point that all stakeholders can see the current state of the project at any point in time through running the latest version of the code.
Market pressure is an important factor when assessing the business value of using agile methods. Time to market can be the decisive factor for the success of a project. Under strong market pressure, a delay of the project completion leads to a loss of market share, which drastically decreases the business value of the project. As market pressure increases, the productivity advantages required strongly encourage choosing an agile process.
A dynamic and ever-changing set of requirements may cause upper management to fear that a project will never be completed. When told that the project will continue as long as the customer identifies high-priority, high-value work, management becomes uncomfortable. Most decision makers like a model in which project budgets are approved and the project remains within the budget confines. However, with agile methods, management can release to production whenever they are ready because with each iteration, the code base has a higher value and is generally more stable than the previous version. Thus, since management sets the priorities, they have complete control of when the project is finished.
One problem the development team may encounter is when a team member likes to create the process artifacts more than code. The other people on the team will quickly assess the value of these activities and will not adopt them if they do not support the overall development effort.

No comments:
Post a Comment